Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: The Silent Threat

Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that can be deadly. Often dubbed the "silent killer," carbon monoxide poisoning can occur quickly and without warning, making it crucial to understand its sources, symptoms, and prevention measures.
Sources of Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide is produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. Common sources include:
- Household Appliances: Gas stoves, water heaters, and furnaces.
- Vehicles: Exhaust from cars and trucks.
- Portable Generators: Especially when used indoors or in enclosed spaces.
- Fireplaces and Wood Stoves: Improper ventilation can lead to CO buildup.
- Charcoal Grills: When used indoors or in garages.
How Carbon Monoxide Affects the Body
When inhaled, carbon monoxide enters the bloodstream and binds to hemoglobin, forming carboxyhemoglobin. This reduces the blood's ability to carry oxygen to cells, tissues, and organs, leading to oxygen deprivation. Prolonged exposure or high levels of CO can result in severe tissue damage and death.

Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
The symptoms of CO poisoning can be subtle and are often mistaken for the flu. They include:
- Mild Exposure: Headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion.
- Moderate Exposure: Symptoms intensify and may include fainting, increased heart rate, and difficulty breathing.
- Severe Exposure: Loss of consciousness, seizures, and death if not promptly treated.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If carbon monoxide poisoning is suspected, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History and Symptoms Review: To identify potential CO exposure.
- Blood Test: To measure the level of carboxyhemoglobin in the blood.
Treatment for CO poisoning includes:
- Immediate Fresh Air: Move the person to fresh air immediately.
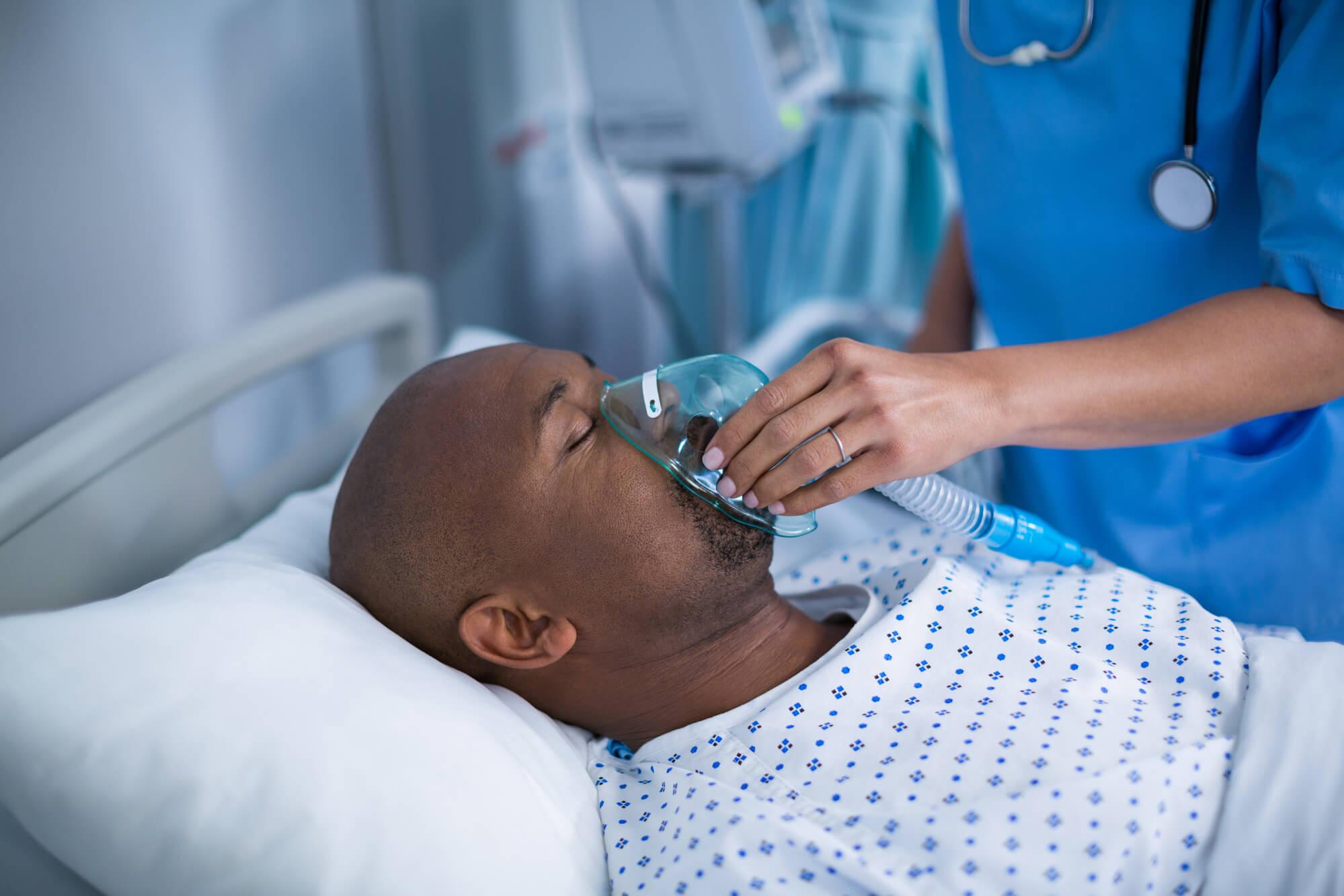
- Oxygen Therapy: Administering 100% oxygen through a mask to quickly reduce CO levels in the blood.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: In severe cases, patients may be placed in a hyperbaric oxygen chamber, which provides pure oxygen at higher-than-atmospheric pressure.
Prevention of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Preventing carbon monoxide poisoning involves several proactive steps:
- Install CO Detectors: Place carbon monoxide detectors near sleeping areas and on every level of your home.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure that all fuel-burning appliances are regularly inspected and maintained.
- Ventilation: Never use gas-powered engines or generators indoors or in poorly ventilated areas.
- Proper Use of Appliances: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the safe operation of all fuel-burning devices.
Awareness and education are critical in preventing carbon monoxide poisoning. By understanding the sources, recognizing the symptoms, and taking preventive measures, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from this silent but lethal threat. Always remember, when it comes to carbon monoxide, vigilance can save lives.


